Lead(II,IV) oxide

 Clash Royale CLAN TAG#URR8PPP
Clash Royale CLAN TAG#URR8PPP Lead(II,IV) oxide, also called red lead is the inorganic compound with the formula Pb3O4. A bright red or orange solid, it is used as pigment, in the manufacture of batteries, lead glass, and rustproof primer paints. It is an example of a mixed valence compound, being composed of both Pb(II) and Pb(IV).[2]
Contents
1 Structure
2 Preparation
3 Reactions
4 Use
5 Physiological effects
6 History
7 See also
8 References
9 External links
Structure
Lead(II,IV) oxide has a tetragonal crystal structure at room temperature, which transforms to an orthorhombic (Pearson symbol oP28, Space group = Pbam, No 55) form at temperature 170 K (−103 °C). This phase transition only changes the symmetry of the crystal and slightly modifies the interatomic distances and angles.[3]
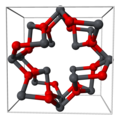
Unit cell of tetragonal Pb3O4
(Key: Pb O)

Part of tetragonal red lead's crystal structure
Preparation
Lead(II,IV) oxide is prepared by calcination of lead(II) oxide (PbO; also called litharge) in air at about 450-480 °C:[4]
- 6 PbO + O2 → 2 Pb3O4
The resulting material is contaminated with PbO. If a pure compound is desired, PbO can be removed by a potassium hydroxide solution:
- PbO + KOH + H2O → K[Pb(OH)3]
Another method of preparation relies on annealing of lead(II) carbonate (cerussite) in air:
- 6 PbCO3 + O2 → 2 Pb3O4 + 6 CO2
Yet another method is oxidative annealing of white lead:
- 3 Pb2CO3(OH)2 + O2 → 2 Pb3O4 + 3 CO2 + 3 H2O
In solution, lead(II,IV) oxide can be prepared by reaction of potassium plumbate with lead(II) acetate, yielding yellow insoluble lead(II,IV) oxide monohydrate, Pb3O4·H2O, which can be turned into the anhydrous form by gentle heating:
- K2PbO3 + 2 Pb(OCOCH3)2 + H2O → Pb3O4 + 2 KOCOCH3 + 2 CH3COOH
Natural minium is uncommon, forming only in extreme oxidizing conditions of lead ore bodies. The best known natural specimens come from Broken Hill, New South Wales, Australia, where they formed as the result of a mine fire.[5]
Reactions
Red lead is virtually insoluble in water and in ethanol. However, it is soluble in hydrochloric acid present in the stomach, and is therefore toxic when ingested. It also dissolves in glacial acetic acid and a diluted mixture of nitric acid and hydrogen peroxide.
When heated to 500 °C, it decomposes to lead(II) oxide and oxygen. At 580 °C, the reaction is complete.
- 2Pb3O4 → 6 PbO + O2
Nitric acid dissolves the lead(II) oxide component, leaving behind the insoluble lead(IV) oxide:
- Pb3O4 + 4 HNO3 → PbO2 + 2 Pb(NO3)2 + 2 H2O
With iron oxides and with elemental iron, lead(II,IV) oxide forms insoluble iron(II) and iron(III) plumbates, which is the basis of the anti-corrosive properties of lead-based paints applied to iron objects.
Use
Lead tetraoxide is most often used as a pigment for primer paints for iron objects. Due to its toxicity, its use is being limited. In the past, it was used in combination with linseed oil as a thick, long-lasting anti-corrosive paint. The combination of minium and linen fibres was also used for plumbing, now replaced with PTFE tape. Currently it is mostly used for manufacture of glass, especially lead crystal glass. It finds limited use in some amateur pyrotechnics as a delay charge and was used in the past in the manufacture of dragon's egg pyrotechnic stars.
Red lead is used as a curing agent in some polychloroprene rubber compounds. It is used in place of magnesium oxide to provide better water resistance properties.
Red lead was used for engineer's scraping, before being supplanted by engineer's blue.
It is also used as an adultering agent in turmeric powder .
Physiological effects
When inhaled, lead(II,IV) oxide irritates lungs. In case of high dose, the victim experiences a metallic taste, chest pain, and abdominal pain. When ingested, it is dissolved in the gastric acid and absorbed, leading to lead poisoning. High concentrations can be absorbed through skin as well, and it is important to follow safety precautions when working with lead-based paint.
Long-term contact with lead(II,IV) oxide may lead to accumulation of lead compounds in organisms, with development of symptoms of acute lead poisoning. Chronic poisoning displays as agitation, irritability, vision disorders, hypertension, and also a grayish facial hue.
Lead(II,IV) oxide was shown to be carcinogenic for laboratory animals. Its carcinogenicity for humans was not proven.

Minium from a mine fire at Broken Hill, Australia
History
This compound's Latin name minium originates from the Minius, a river in northwest Iberia where it was first mined.
Lead(II,IV) oxide was used as a red pigment in ancient Rome, where it was prepared by calcination of white lead. In the ancient and medieval periods it was used as a pigment in the production of illuminated manuscripts, and gave its name to the minium or miniature, a style of picture painted with the colour. As a finely divided powder, it was also sprinkled on dielectric surfaces to study Lichtenberg figures.
In traditional Chinese medicine, red lead is used to treat ringworms and ulcerations, though the practice is limited due to its toxicity. Also, azarcón, a Mexican folk remedy for gastrointestinal disorders, contains up to 95% lead(II,IV) oxide.[6]
See also
- Lead paint
Lead(II) oxide, PbO
Lead(IV) oxide, PbO2- List of inorganic pigments
References
^ "VOLUNTARY RISK ASSESSMENT REPORT ON LEAD AND SOME INORGANIC LEAD COMPOUNDS". Retrieved 2012-12-25.
^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 0-08-037941-9.
^ Gavarri, J; Weigel, Dominique; Hewat, A. W. (1978). "Oxydes de plomb. IV. Évolution structurale de l'oxyde Pb3O4 entre 240 et 5 °K et mécanisme de la transition" [Lead oxides. IV. Structural evolution of the oxide Pb3O4 between 240 and 5 K and mechanism of transition]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry. 23 (3–4): 327. doi:10.1016/0022-4596(78)90081-6.
^ Carr, Dodd S. (2005), "Lead Compounds", Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, doi:10.1002/14356007.a15_249
^ Minium
^ Bose, A.; Vashistha, K; O'Loughlin, B. J. (1983). "Azarcón por empacho – another cause of lead toxicity". Pediatrics. 72: 108–118.
External links
- National Pollutant Inventory - Lead and Lead Compounds Fact Sheet
- Minium mineral data
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
Preferred IUPAC name Lead tetroxide [1] | |
| Other names Minium, red lead, triplumbic tetroxide | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
ChemSpider |
|
ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.851 |
EC Number | 215-235-6 |
PubChem CID |
|
UN number | 1479 |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula | Pb 3O 4 |
Molar mass | 685.6 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | Vivid orange crystals |
Density | 8.3 g cm−3 |
Melting point | 500 °C (decomposition) |
Vapor pressure | 1.3 kPa (at 0 °C) |
| Structure | |
Crystal structure | Tetragonal, tP28 |
Space group | P42/mbc, No. 135 |
| Hazards | |
GHS pictograms |    |
GHS signal word | DANGER |
GHS hazard statements | H272, H302, H332, H360, H373, H410 |
GHS precautionary statements | P201, P220, P273, P308+313, P501 |
NFPA 704 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Infobox references | |
Lead compounds | |
|---|---|
| Pb(II) |
|
| Pb(II,IV) |
|
| Pb(IV) |
|




Comments
Post a Comment